Model question Soluation of Economic 2079
1. Define opportunity cost?
-the second best alternative that has been sacrificed by economy agent while taking an economy decision is know as opportunity cost.
2. Define Socialist economy?
-The economy in which production , distribution , investment etc. are owned and controlled by state in the interest of society is called Socialist Economy.
3. What is Market?
-Market is a system where buyers and sellers come into contract for the transaction of goods and services.
4. What is market equilibrium?
- It is the state in which market supply and demand balance each other and as a result prices become stable.
5. What are the two conditions for firm to be in equilibrium?
-Its profit should be maximum
-Marginal cost should be equal to marginal revenue
6. What is mean by Factor pricing?
-In economic theory, a factor pricing is the unit cost of using a factor of production such as labour or physical capital.
7. Define Bank?
-The financial institution which deals with the money and credit is known as bank .
8. What are internal and external source of government revenue?
- External source of government revenue
-Bilateral Borrowing
-Multilateral Borrowing
- Internal source of Borrowing
- Market borrowing
- Non market borrowing
9. Define government revenue?
- Government revenue means the income of government from various sources like tax and non-tax.
10. Define International trade?
- International trade refers to the exchange of goods and services between different countries.
Short answer Questions.
11. Write short notes on scarcity and choice?
Scarcity
- Scarcity refers to the condition of insufficiency where human beings are incapable to fulfill their wants in a sufficient manner. In other words, it is a situation of fewer resources in comparison to unlimited human wants. Human wants are unlimited. We may satisfy some of our wants but soon new wants arise. It is impossible to produce goods and services so as to satisfy all the wants of people. Thus scarcity explains this relationship between limited resources and unlimited wants and the problem therein.
Economic problems arise due to scare goods. These scare goods have many alternative uses. For example, land can be used to construct a factory building or to make a beautiful park or to raise agricultural crops. So, it is very essential to think about how limited resources can be used alternatively to satisfy some wants of people to get maximum satisfaction as possible.
Choice
- The choice is the process of selecting a few goods or wants from the bundles of goods or wants. Human wants are unlimited. So, they are unable to fulfill all their wants at once. They can satisfy only some of their wants. Some wants should be sacrificed to get some other wants. Hence, people postponed less urgent wants to satisfy more urgent wants. For example, a boy desiring to buy a book does not visit the cinema hall. Thus, the problem of choice deals with the utilization of scarce resources in such a way that it satisfies human wants in the best possible way. If human wants were limited or resources were unlimited, then, there would be no scarcity and there would be no problem of choice. Because of scarcity, we are forced to choose.
12. Define Capitalist economy? What are the features of capitalist economy.( Market Economy)
- Capitalist economy is often thought of as an economic system in which private sector own and control property in accord with their interests, and demand and supply freely set prices in markets in a way that can serve the best interests of society.
*Features of Capitalist economy
a. Private Property
- In the capitalist economy, all the means of production like, land, capital and equipment belongs to individuals and firms. This types of property can be further extended in the process of production.
b. Economic Freedom
- The market economy belongs on free economic activities. it means a person can do entirely economic activities such as consumption, saving, production of goods , establishment of new industry.
c. Profit Motive
- In this system every producer, consumer, and trader is free to use their skill and property for their own benefit
d. Price Mechanism
- Price Mechanism guided to the consumer what goods and services consumer would demand in hot quantity? the price to system helps to producer what to produce in what quantity.
13. Define Monopoly market? What are the features of monopoly market?
- Monopoly is a market structure where there es only one seller or producer and large number of buyers. In this type of market there is no close substitute of the commodity that these seller sells. The seller has full control over the supply of commodity
*Features of monopoly market
a. single seller and large no of buyers
- There is a single firm producing the commodity in the market but the no of buyers is assumed in the large in monopoly.
b. No close substitute
- There is no close substitute goods available in the market.Monopoly can't exits when there is competition as well as close substitute goods are available in the market
c. Barrier to entry on new firm
- In the monopoly market, there is complete barrier to the entries of new firm. if new firm entries to the market, monopoly itself break down.
d. Independent price policies
- The monopoly firm can adopt independent price policy, that is it can increase or decrease the price as it likes.
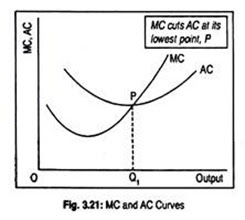
14. Show the relationship between average cost and marginal cost?
- AC is obtained by dividing total cost by units of output produced.
- MC is defined as the change in total cost due to one unit change in output produced.
We can represent both AC and MC in the following figures,
With the help of above figure, we can derived the following relationship between AC and MC
- Both AC and MC are derived from same sources TC and label of output Q. with the difference that MC needs change of its TC and Q.
- Both are U-shaped due to the law of variable proportion.
- When AC is falling, MC curve lies below and MC falls faster than AC.
- MC cuts AC at its minimum point
15. Explain the Uncertainty theory of profit?
This theory is propounded by Knight. According to this theory, profit is reward for bearing uncertainty. Uncertainty is due to unforeseeable or non insurable risk. According to knight, there are two types of risk. They are foreseeable and unforeseeable. The possible loses due to foreseeable risk is avoidable with insurance. Therefore, the risks are insurable risk but possible loss due to unforeseeable risk is not avoidable with insurance. Therefore, the risks are non foreseeable risk. There are mainly four types of non insurable risk. They are
a. Risk due to competitors:
Any business firm has the risk due to increase in number of competitors, change in their marketing strategies, improvement in their quality and management, decrease in their cost of production per unit etc. This risk is not avoidable with insurance.
b. Risk due to change in policy of government:
The government may change its policy related to investment, export, import, taxes, and so on. Due to it, any firm may suffer loss. This risk is not avoidable with insurance.
c. Risk due to trade cycle:
During recession and depression, most of the business firms suffer loss. This risk is not avoidable with insurance.
d. Risk due to technological change:
Technology advances with flight of time. If any firm fails to adjust the change in technology, the firm suffers loss. This risk is also not avoidable with insurance.
Criticisms
a. Not direct relation between profit and uncertainty:
Profit is not directly related to uncertainty. If the business involves high risk, there is more probability of failure and loss rather than profit.
b. Profit is reward for avoidance of uncertainty:
Profits earned only if uncertainty is successfully avoided using skills, education, knowledge, experiences and so on. It is not earned mere taking uncertainty.
c. Uncertainty is not factor of production:
According to this theory, uncertainty seems to be the factor of production but factor of production is organization not uncertainty.
d. Reward for all things performed by organization:
Organization earns profit not only taking uncertainty but for all things it performs. They are innovation, effective combination of inputs, use of skills knowledge etc. and bargaining power.
16.Wage fund theory of wage
This theory is developed by classical economist named J.S Mill. According to Mill, wage level is determined by wage fund and the number of worker’s employed. To pay the laborer, a wage fund is raised. Once the wage fund id rose, it is kept constant. The wage fund is distributed among the worker’s employed. The workers are assumed to be paid equal amount. It is because the units of labor are homogeneous. If more workers are employed each worker gets fewer amounts and if less number of workers is employed each worker gets more amount of money. The wage level is given by the ratio of wage fund and number of worker’s employed.
Mathematically,
This theory can be explained with the help of table and figure as following:
| Wage fund (W.F) | No. of workers (N) | Wage level (W.F/N) |
| Rs 1,00,00,000 | 50000 | Rs 200 |
| Rs 1,00,00,000 | 100000 | Rs 100 |
| Rs 1,00,00,000 | 150000 | Rs 66.67 |
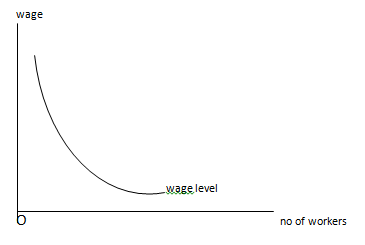
In the above table, wage fund raised is Rs 1, 00, 00,000. When the number of workers employed is increased from 50000 to 100000 and 150000 the wage level is decreased from Rs 200 to Rs 100 and Rs 66.67 respectively. It is due to constant wage fund distributed among more workers. If we represent wage level with respect to number of workers employed we obtain a convex curve.
In the above figure, the downward sloped convex curve represents inverse relationship between wage level and no of workers employed.
Assumptions
- a. According to this theory, wage fund is rose before the employment of workers
- b. The workers are paid equally out of the wage fund
- c. The units of labor are homogeneous
- d. The wage level is flexible to the change in number of workers employed
- e. Money is just a medium of exchange
Criticisms
- a. Wage fund is not raised before employing the workers but is rather raised on the basis of worker’s employed
- b. Wage paid to workers differs from place to place, time to time, person to person and organization to organization.
- c. Units of labor are not homogeneous. They differ in skill, knowledge, strength, education, attitude etc.
- d. Wage level is not flexible. Wage level fall is opposed by workers and trade unions
17. What are the advantage and disadvantage of free trade ?
- Free trade is the policy in which flow of goods and services are allowed without any government or international organization barriers.
Advantages of a Free Trade Area
A free trade area offers several advantages, including:
1. Increased efficiency
The good thing about a free trade area is that it encourages competition, which consequently increases a country’s efficiency, in order to be on par with its competitors. Products and services then become of better quality at a lower cost.
2. Specialization of countries
When there is intense competition, countries will tend to produce the products or goods that they are most efficient at. Efficient use of resources means maximizing profit.
3. No monopoly
When there is free trade, and tariffs and quotas are eliminated, monopolies are also eliminated because more players can come in and join the market.
4. Lowered prices
When there is competition, especially on a global level, prices will surely go down, allowing consumers to enjoy a higher purchasing power.
5. Increased variety
With imports becoming available at a lower cost, consumers gain access to a variety of products that are inexpensive.
Disadvantages of Free Trade Area
Despite all the benefits brought about by a free trade area, there are also some corresponding disadvantages, including:
1. Threat to intellectual property
When imports are freely traded, domestic producers are often able to copy the products and sell them as knock-offs without fear of any legal repercussions. Therefore, unless the FTA includes provisions for intellectual property laws and enforcement there are no protections for exporting companies.
2. Unhealthy working conditions
Outsourcing jobs in developing countries can become a trend with a free trade area. Because many countries lack labor protection laws, workers may be forced to work in unhealthy and substandard work environments.
3. Less tax revenue
Since member countries are no longer subject to import taxes, they need to think of ways to compensate for the reduced tax revenue.
4. Economic Dependency
- Due to free trade, a country doesn't produce all the necessary goods rather, it imports the goods and services which are not possible to produce economically. This situation creates economic dependency.
18. Distinguish between economic rent and contract rent?
The following are the differences between economic rent and contract rent:
Difference # Economic Rent:
1. It is imaginary and theoretical concept of rent.
2. It is calculated on the basis of the difference between the cost of super-marginal land and cost of marginal land.
3. It increases with the decrease in the produce of marginal land and decreases with the increase in the produce of marginal land.
4. It does not exploit the tenants as there is no high rent because no marginal land exists.
Difference # Contract Rent:
1. It is a practical and realistic concept.
2. It is determined between landlord and cultivator on the basis of economic forces of demand and supply.
3. It is not affected by the change in the produce of marginal land and it is affected by the contract deed between the landlord and the tenants.
4. There is chances of exploitation of peasants when demand for land increases.
19.Distinguish between money wage and real wage
Money wage
- It is the reward obtained by a labourer in terms of cash or money for his/her service deliver in production process
- It is expressed in monetary process
- Excludes additional benefits given to the labourers.
- It is narrow concept.
Real Wage
- Real wage is the reward obtained by a labourer in term of goods and services and services for his/her service rendered in production process.
- It is expressed in real term.
- It include additional benefits given to the labourer .
- It is a board concept.
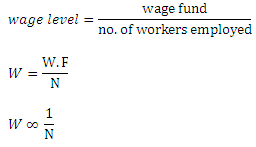
Comments
Post a Comment